Sofia University Synthesizing Air Quality Data with Cesium
The Urban Data Project, developed by the GATE Institute at Sofia University, is tracking air quality data in Sofia with a CesiumJS application.
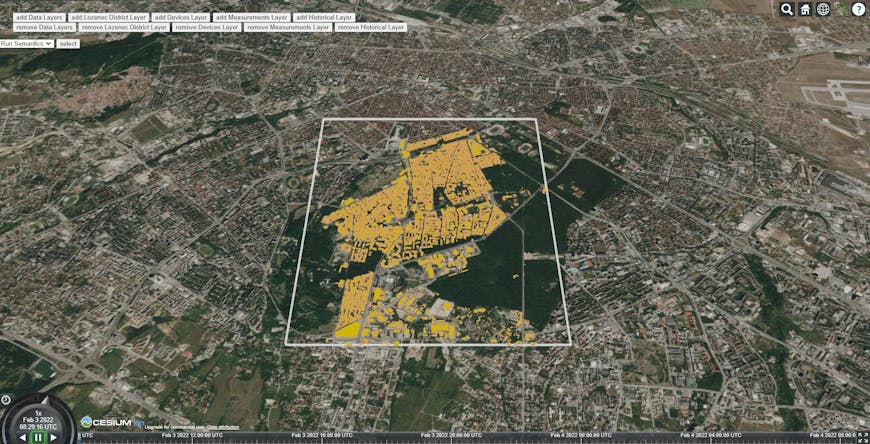
The Urban Data Project includes a 3D model of the city of Sofia.
The Urban Data Project supports better air quality monitoring and environment-aware urban planning. With Cesium, they’ve been able to integrate static models of the urban infrastructure with dynamic information from the environment.
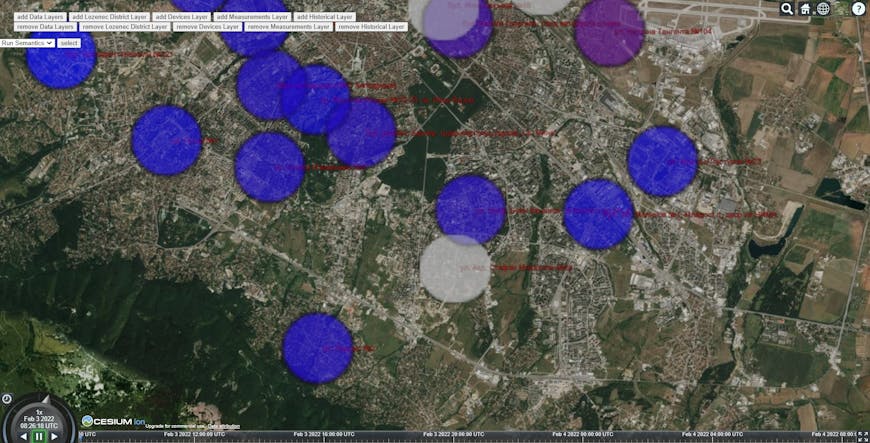
The application provides data on air pollution from various sensor stations throughout the city.
Air quality sensors throughout the city have been in place for some time, but that data has been fragmented in various applications. The Urban Data Project migrated these various applications to GATE’s platform for data processing on their private cloud. That migration required integrating information from multiple sources, including sensors, databases, and interactive models, which was all in different formats, e.g., JSON, SQL, KML, RDF. Those datasets were also ingested in different modes of delivery, including streaming, messaging, file uploads, database imports), and stored in different repositories, e.g., SQL databases, NoSQL databases, GML databases, graph databases, distributed file systems.
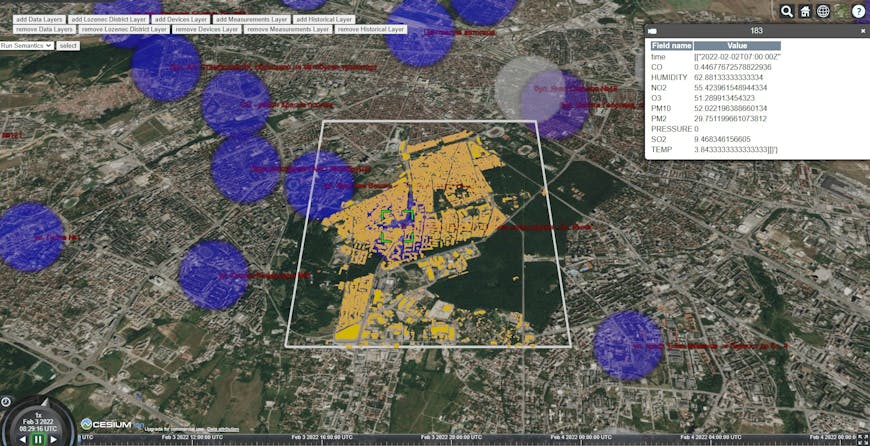
Users can get more detailed information from each sensor, updated in real time.
By integrating all the data and providing a simple, intuitive user interface built on CesiumJS, the GATE Institute made the data more accessible and simplified navigation so users can quickly find relevant data around buildings, streets, and transport routes.
To get started building your own application, sign up for a Cesium ion account.